Facts about the project
PhD project: Johannes Mair +++ Duration: 01.06.2021– 31.12.2024 +++ Project funding: Bundesamt für Strahlenschutz (BfS), Berlin


As a result of the decay of radon and its decay products, the resulting ionizing radiation causes damage to DNA and cell structure and can thus cause cancer. In the vicinity of faults, increased radon levels in the soil air can occur and lead to an increased hazard potential. In order to better assess the significance of such local anomalies for the determination of radon precautionary areas, an area with active tectonics will be investigated in greater detail within the framework of a pilot project. For the working area near Riedstadt west of Darmstadt, a three-dimensional structural model is to be generated by combining a variety of geological and geophysical methods, which will provide a detailed representation of the subsurface structures and, in particular, the geometry of the faults. In addition to the development history of the faults, the migration paths of radon in particular should thus be better understood.
- Geophysical surveys successfully completed.
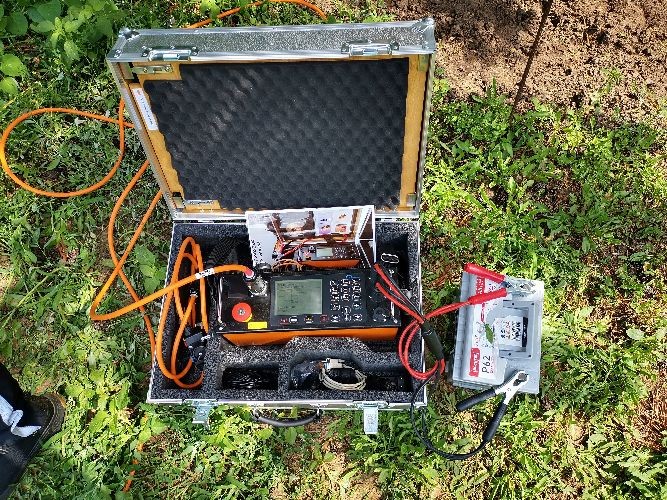
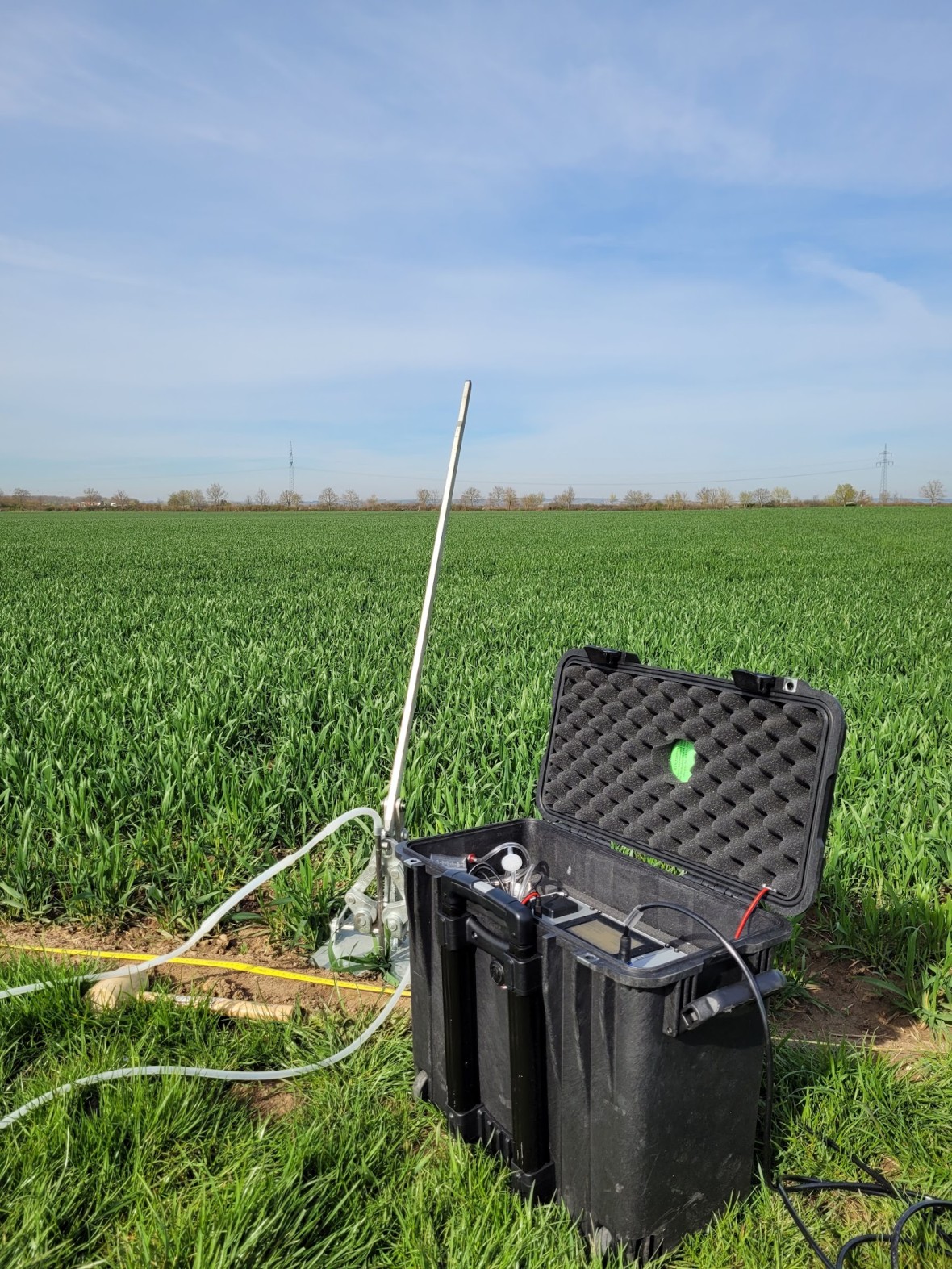
- 600 active radon soil air measurements and 200 exposimeter measurements conducted.
- Laboratory measurements on soil samples and 100 alpha spectrometric evaluations performed.
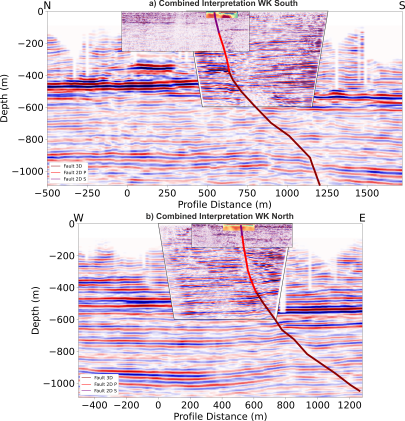
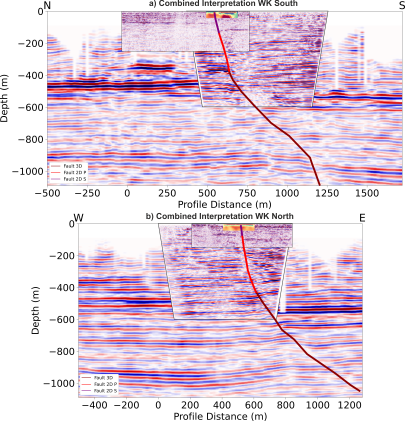
Mapping of Active Faults
Active faults were successfully mapped from several kilometers deep to just a few meters below the Earth's surface. These results provide strong evidence of neotectonic activities in the studied area.
Modeling of Radon Activity Concentrations
Currently, the measured radon activity concentrations along profiles crossing faults are being analyzed using machine learning models. The goal is to explain the variability of radon concentrations.
Influencing Factors on Radon Activity Concentrations
Initial results indicate that, in addition to fault zones, other factors such as soil types/grain size and weather conditions influence radon activity concentrations. It becomes clear that the signal from fault zones must be initially isolated from these additional influencing factors to establish clear correlations.
Picture Gallery
-
![]()
Messkampagne – P-Welle. -
![]()
Messkampagne – P-Welle. -
![]()
Messkampagne – P-Welle. -
![]()
Messkampagne Radonmessungen. -
![]()
Messkampagne Radonmessungen. -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle (LIAG). -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle (LIAG). -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle (LIAG). -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle (LIAG). -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle (LIAG). -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle (LIAG). -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle/ Geoelektrik (TUDa). -
![]()
Messkampagne S-Welle/ Geoelektrik (TUDa). -
![]()
aMesskampagne S-Welle/ Geoelektrik (TUDa).
- Go to picture 1
- Go to picture 2
- Go to picture 3
- Go to picture 4
- Go to picture 5
- Go to picture 6
- Go to picture 7
- Go to picture 8
- Go to picture 9
- Go to picture 10
- Go to picture 11
- Go to picture 12
- Go to picture 13
- Go to picture 14
Publications
- Platz, A., Weckmann, U., Pek, J., Kováciková, S., Klanica, R., Mair J., & Aleid B.: 3D imaging of the subsurface electrical resistivity structure in West Bohemia/Upper Palatinate covering mofettes and Quaternary volcanic structures by using magnetotellurics. (in preparation).
Conference Contributions
- Mair, J., Petermann, E., Lehné, R., Henk, A.: Deciphering Radon Variability in the Northern Upper Rhine Graben: An Analysis Using Passive and Active Detection with Random Forest Modelling, EGU General Assembly 2024, Vienna, Austria, 14–19 Apr 2024, EGU24-16925, https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu24-16925, 2024.
- Lehne, R., Daum, J., Mair, J., Heggemann, H., Hoselmann, C., Henk, A.: Observation and geological interpretation of the longest vertical radon profile to date: variability of radon concentrations along a 323 m deep drilling, EGU General Assembly 2024, Vienna, Austria, 14–19 Apr 2024, EGU24-21822, https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu24-21822, 2024.
- Mair, J., Buness, H., Henk, A., Lehné, R., Tanner, D. C.: Imaging neotectonic faults in the Northern Upper Rhine Graben using a multi-method geophysical approach, at 84th DGG Annual Meeting, 10–14 March 2024, Jena.
- Mair, J., Henk, A., Buness, H., Lehné, R., Tanner, D. C.: Multi-Geophysical Imaging of Neotectonic Faults in the Northern Upper Rhine Graben, at TSK20 in Freiburg, 17.-22.03.2024, 20th Symposium Tectonics, Structural Geology, and Geology of Crystalline Rocks.
- Mair, J., Henk, A., Lehné, R.: Soil properties and weather conditions mask a potential tectonic contribution to radon concentrations measured in soil air – a case study from the northern Upper Rhine Graben, EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 Apr 2023, EGU23-13566, https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu23-13566, 2023.
- Mair, J., Lehné, R., Henk, A.: Radonanomalien in der Bodenluft und die Tiefenstruktur von Störungen, bei der Klausurtagung der Strahlenschutzkommission, Mainz.
- Mair, J., Buness, H., Henk, A., Lehné, R., Röhlinger, L.: Multi-Method Geophysical Investigation of Fault Structures in the Northern Upper Rhine Graben: Insights from the NeoNORG Project, GeoBerlin 2023, DOI: 10.48380/v4kn-wa41.
- Mair, J., et al.: Untersuchung des Einflusses von Störungszonen auf Radonaktivitätskonzentrationen in der Bodenluft: Erkenntnisse aus dem NeoNORG-Projekt, at StrahlenschutzGespräch Radon 2023, Berlin, 18. und 19. Oktober 2023.
- Aleid, B., Weckmann, U., Platz, A., Mair, J.: Magnetotellurics in the Eger Rift: Regional and local three-dimensional subsurface imaging and modelling of fluid pathways from the crust-mantle boundary to the surface, EGU General Assembly 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022, EGU22-4884, https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu22-4884, 2022.
- Mair, J., Lehné, R., Henk, A., Buness, H., Hoselmann: Radon anomalies in soil gas and faults in quarternary sediments – a case study from the Upper Rhine Graben using near-surface geophysical methods, at TSK19 in Halle, 17.-23.03.2024, 19 Symposium Tectonics, Structural Geology, and Geology of Crystalline Rocks.
- P-Wave Seismics:
- Provided and conducted by the Leibniz Institute for Applied Geophysics (LIAG) with support from the Technical University of Darmstadt (TU Darmstadt).
- Shear Wave Seismics:
- Partly conducted by LIAG with support from TU Darmstadt and partly independently by TU Darmstadt.
- Radon Measurements:
- Instrumentation and analysis support:
- Radon measurement devices: Funded and provided by the Hessian Agency for Nature Conservation, Environment, and Geology (HLNUG) and the Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS).
- Laboratory evaluations: Supported by HLNUG and BfS for exposimeters and alpha spectrometry.
- Instrumentation and analysis support:
- 3D Seismic Data: Provided by Rhein Petroleum.
Status Quo
Radon Measurements:
Both the 600 active radon soil air measurements and the 200 exposimeter measurements are completed.
Geophysical Surveys:
All planned methods (P-wave seismics, S-wave seismics, geoelectric, ground-penetrating radar) were conducted, mapping active faults and proving neotectonic activities.
Laboratory Measurements:
Analysis of soil samples and 100 alpha spectrometric evaluations have been performed.
Outlook
Continuation of analysis using machine learning models to explain radon variance, considering fault zones, soil conditions, and weather conditions.




















